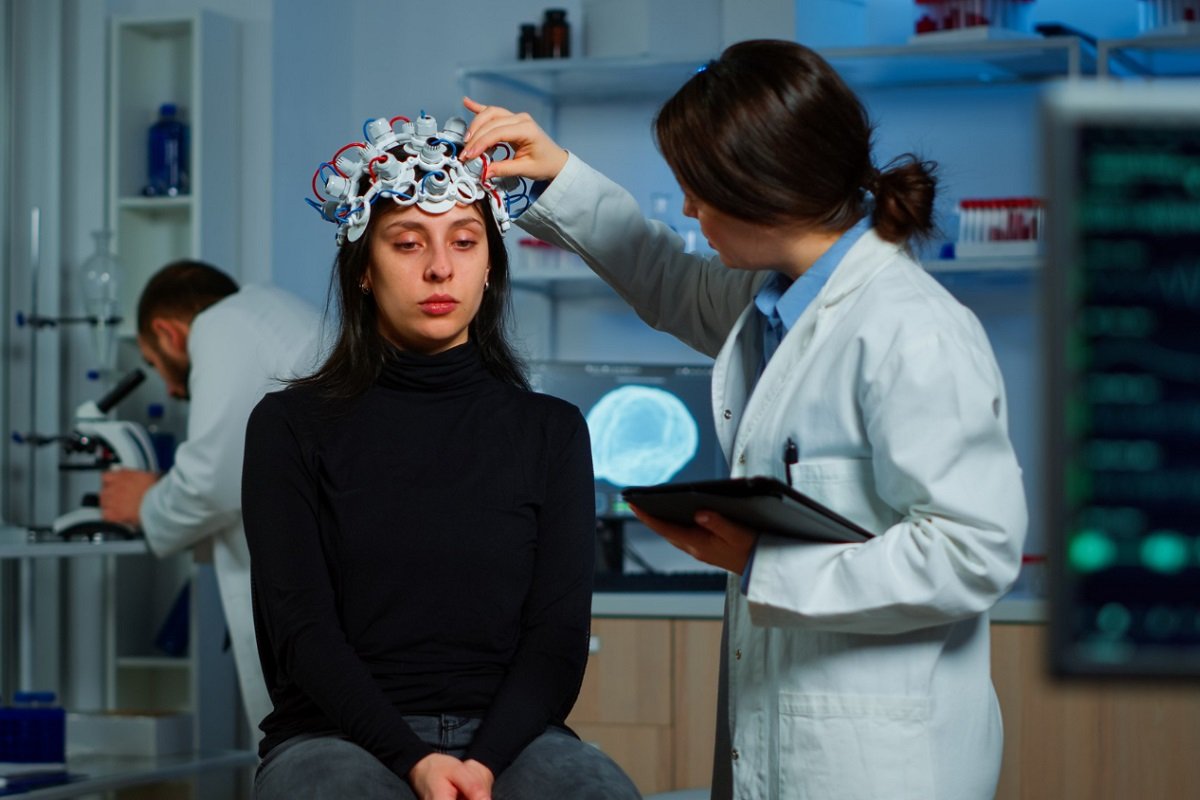
EEG technology is playing a significant role in changing the diagnostic perspective of mental disorders to evidence-based for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
Mental health is one area that has been changing over the decades and beyond because of constant scientific and technological advancements.
One of such tools is EEG technology that evidently measures voltage fluctuation from the human brain and is one of the tools that are rapidly changing the ways in which mental disorders are diagnosed and treated.
EEG technology that was initially employed in research and neurology for epilepsy and sleep disorders has recently been adapted to psychiatry and psychology to avail greater understanding of mental health disorders.
5 Ways EEG Technology is Transforming Mental Health Diagnostics
Here in this blog post, we are going to discuss how EEG equipment is redefining mental health diagnosis so that the practitioners can diagnose the conditions with better precision as well as treat them according to the patient’s needs while significantly enhancing the quality of care that they facilitate.

1. Understanding EEG Technology
EEG is an invasive technique that is used to capture electrical occurrences in the brains of patients. An EEG machine involves having electrodes placed on the scalp to record the brain waves, after which such information is converted into graphical form for the clinicians to study. This technology captures the alpha, beta, deep, theta, and gamma waves, which are associated with different brain activities and conditions.
For many years, EEG has been used in hospitals to identify several disorders, including epilepsy, the presence of tumours in the brain, and sleep disorders. But with new techniques in neuroimaging and data analytics, it has expanded the possibility into mental health, where clinicians can evaluate the function of the patient’s brain in depression, anxiety, ADHD, schizophrenia, and more.
Also Read: What Does a Drug Addiction Treatment Program in Utah look like?
2. EEG and Mental Health: A New Frontier
EEG has been adopted comparatively recently in mental health yet its application is now rapidly growing. Psychiatric diseases usually present diagnostic challenges due to their intrinsic and relatively reliance on the patient report and the clinician’s observation. Hence, more prominent traditional techniques could be questionnaires supplemented with interview significantly restricted by biases and multifactorial nature of symptoms. EEG technology fits this gap as it offers quantifiable data of brain activity and capabilities rather than a comprehensive account of the patient’s mental health.
a. Depression and Anxiety
Indeed, depression and anxiety are two of the most common mental disorders in the world today, but the diagnosis of the disorders cannot be done easily since the symptoms are sometimes similar. EEG technology is making clinicians better appreciate these disorders given the patterns of brain waves that manifest themselves in relation to emotions and how the brain is wired.
For instance, in depressed persons, the part of the brain related to mood control—the left prefrontal cortex—has been found to have less activity. Through the assessment of the EEG data, the clinicians are in a position to realize these patterns ahead of time when the signs have not reached an extreme level.
Consequently, it has been used to analyse anxiety based on the enhanced circuitry in the beta waves in the brain or the arousal system. Several studies have shown its applicability in differentiating between different forms of anxiety disorders, as well as in evaluating the effectiveness of such therapies as CBTs and medicines.
b. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
ADHD is a health condition that consists of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, and this disorder is also being diagnosed with EEG. These children and adults with the disorder have impaired patterns of theta and beta waves of the brain. A low-amplitude theta wave pattern is best seen in sleep and absentmindedness, while a high-amplitude beta wave is seen in wakefulness and concentration. EEG in typical ADHD also reveals a high theta-to-beta ratio as a sign that the condition exists.
Normal diagnosis of ADHD includes interviews, questionnaires, and observation of behavior, while EEG seems to be more objective. Currently, some clinicians are beginning to utilize EEG-based tests in order to determine how their patients react to things such as stimulant medications or specific forms of behavioral therapy.
c. Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia could also be another mental disorder that would benefit from use of EEG technology. Schizophrenia patients have been found to have impaired brain wave activity in theta and gamma range that have impact on memory, attention and perceptual processes.
EEG is employed in the investigations of these disruptions and the knowledge of early markers of schizophrenia is of immense value as the latter: as is well known, early diagnosis of a disease is pivotal in the treatment process. Such particular patterns Examining Brainwave activity associated with Schizophrenia can help the clinicians trace the further advancement on the disease and make requisite amendments to the ongoing treatment regimens.
3. Personalizing Mental Health Treatment with EEG
Another advantage that EEG has over other mental health technologies is its ability to create one-on-one outcomes for patients. Common medications for mental illnesses, like depression or schizophrenia, can be recommended by a trial-and-error method. People do not get relief from their symptoms for weeks or even months, and what is more frustrating is that they cannot choose the treatment themselves.
EEG can modify this by affording clinicians help to know the kind of treatment a patient with a particular condition needs due to the different response of the brain. For instance, EEG can indicate the way the brain responds to various treatments so that practitioners could find out which medication may be best for a certain patient. This reduces time spent on experiments as well as shortens the overall time a patient takes to heal.
Other areas of individualized treatment that also hold significant potential include EEG-based neurofeedback. Neurofeedback is a type of treatment that works with the patient to control his brain waves with the help of information about the activity of the brain. For instance, people suffering from anxiety or depression can be trained to enhance or dampen certain brain waves linked with the sickness. Over some time, it means the person’s mental condition is becoming better and the severity of the symptoms slowly begins to reduce.
4. EEG and the Future of Mental Health Diagnostics
This is due to the fact that with advancement in EEG technology, its uses in mental health disorder diagnoses are likely to increase. Anticipating the potential benefits of future roles in EEG analysis is interesting, but there may be one area more intriguing: the advantage of artificial intelligence in machine learning algorithms. Specifically, these algorithms can work with big databases of EEG information while outlining some nuances that might remain unnoticed by the human observer. This could lead to even more timely identification of mental health diseases, not to mention more precise ones.
Also, new and lightweight EEG sensors created for portable and even wearable use make it possible for patients to conduct regular brain activity tests at home. It may also be a beneficial source of information for clinicians in between sessions and can transform patients into an active status as they play in their wellness.
EEG is also expected to have an important role in the evaluation of the brain’s response to the new therapies TMS and DBS. Through using EEG in these treatments, it is likely to achieve the best therapy and patients’ results as well.
5. Challenges and Limitations
Nevertheless, problems are inherent in any technology, including EEG technology that is used in mental health diagnostics. EEG records electrical activity on the scalp, which means that it can only register activities from the surface of the brain and not deeper in the brain where some disorders we know of occur. Also, the analysis of EEG data is quite complex, and often only a few centers have specialists who can decode it.
Another challenge is cost since the EEG equipment and the software for analyzing the results may be costly. But since the usage of the technology is still in its early days and is bound to become cheaper with time, these challenges should eventually fade as the technology evolves.
Conclusion
New EEG technology promises to improve the accuracy and individuality of diagnosis and treatment of mental health disorders. Starting from the screening of depression and anxiety through to individual approaches to ADHD and surveillance of schizophrenia, EEG is adding to the understanding of the brain. Maintaining this movement and the involvement of AI as well as portability of devices, EEG is poised for the future as a more formidable modal for changes in mental health care.
Mental health diagnostics has a very bright future and EEG is one of the leading technologies in this new paradigm shift.
Follow Us on Facebook for more: eeg technology related updates.